Introduction
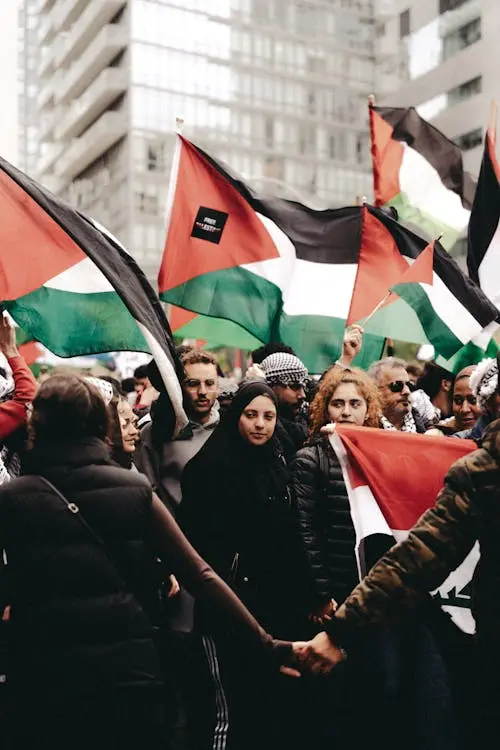
Over the past week, more than 1,000 protesters have been arrested at pro-Palestinian demonstrations on college campuses across the United States. This wave of activism—comprising students, faculty members, and community allies—has sparked heated debates about freedom of speech, academic freedom, and the role of universities in political discourse. While these protests call for divestment from Israel and solidarity with Palestinian rights, they also shed light on the broader issues of civil liberties and institutional response to dissent.
In this blog post, we will delve into the recent surge of campus protests, exploring the reasons behind them, the key locations where they have occurred, and the implications for both academic communities and broader society. Whether you’re a student, an activist, or simply concerned about these developments, join us as we navigate this complex and pressing issue.
The Surge of Campus Protests
The Catalyst: Heightened Tensions
The recent escalation of violence in Gaza and broader Middle Eastern conflicts has galvanized student activists across the nation. These events have intensified calls for university administrations to reconsider their financial and academic relationships with Israel. The demand for divestment has been a central issue, with students urging their institutions to withdraw investments from companies and governments that they believe are complicit in human rights violations.
A Diverse Coalition
One of the most striking features of these protests is the diversity of the participants. Students from different ethnic, religious, and academic backgrounds have united in their call for justice. Faculty members and staff have also joined the movement, highlighting a broader consensus within the academic community. This coalition underscores the intersectionality of the issue, linking Palestinian rights to broader struggles for social justice and equality.
The Role of Social Media
Social media has played a crucial role in organizing and amplifying these protests. Platforms like Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok have been used to share information, coordinate actions, and document encounters with law enforcement. The hashtag #FreePalestine has trended globally, drawing attention to the movement and rallying support from around the world.
Key Locations of Protest
New York University (NYU)
At NYU, hundreds of students and faculty members staged a sit-in at the university’s administration building. The protest, which lasted several days, called for immediate divestment from companies that do business with Israel. The university’s response, which included police intervention and several arrests, has sparked a wider debate about the limits of peaceful protest and the role of higher education institutions in political activism.
University of California, Berkeley
Berkeley, known for its history of student activism, has seen some of the largest and most intense protests. Demonstrators blocked major streets, occupied administrative offices, and held teach-ins to educate the campus community about the Palestinian struggle. The arrests at Berkeley have drawn significant media attention, highlighting the ongoing tension between student movements and university authorities.
Harvard University
At Harvard, students organized a series of rallies and marches, demanding that the university cut ties with companies involved in the Israeli occupation. The administration’s response, which included increased police presence and restrictions on campus gatherings, has been met with criticism from both students and faculty. The situation at Harvard illustrates the growing chasm between student activists and institutional policies.
The Broader Implications
Freedom of Speech and Academic Freedom
The mass arrests of protesters have raised serious questions about freedom of speech on college campuses. Critics argue that the crackdown on protests stifles dissent and undermines the principles of academic freedom. Universities, traditionally seen as bastions of free thought and debate, now face scrutiny over their handling of political activism.
Impact on University Policies
The protests have also prompted a re-evaluation of university policies regarding investment and engagement with foreign governments. Some institutions have already begun reviewing their portfolios, while others face increasing pressure from their communities to take a stand. The outcomes of these reviews could have significant financial and ethical implications for the universities involved.
Community and Solidarity
These protests have fostered a sense of solidarity among students, faculty, and community members. The shared experience of activism has strengthened bonds within the academic community and beyond. This solidarity is not only a source of support for those involved but also a powerful reminder of the collective power of grassroots movements.
Practical Tips for Student Activists
Know Your Rights
Understanding your legal rights is crucial when participating in protests. Familiarize yourself with local laws regarding peaceful assembly and free speech. Organizations like the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) offer resources and guidance for activists.
Stay Informed
Keep abreast of developments in the Middle East and related political issues. Staying informed will help you articulate your position and respond to counterarguments effectively. Reliable news sources and academic journals can provide valuable insights.
Build Alliances
Form alliances with other student groups, faculty members, and community organizations. A united front can amplify your message and provide a broader base of support. Collaboration can also bring diverse perspectives and strategies to your movement.
Examples of Successful Student Activism
The South African Divestment Movement
The anti-apartheid movement of the 1980s saw significant student activism that led to widespread divestment from companies operating in South Africa. This movement is often cited as a successful example of how student protests can effect change in university policies and contribute to broader social justice efforts.
Fossil Fuel Divestment Campaigns
In recent years, student-led campaigns for fossil fuel divestment have gained traction. Many universities have committed to divesting from fossil fuels, demonstrating the power of sustained student activism. These campaigns highlight the potential for student movements to address global issues like climate change.
Black Lives Matter on Campus
The Black Lives Matter movement has inspired numerous campus protests addressing racial injustice and police violence. These protests have led to tangible changes, such as the removal of statues and renaming of buildings, showing how student activism can impact institutional practices.
Challenges and Considerations
Balancing Academics and Activism
Students often face the challenge of balancing their academic responsibilities with their activism. Effective time management and prioritization are key to maintaining this balance. Many activists find that their academic work can complement their activism, providing a deeper understanding of the issues they are passionate about.
Navigating Institutional Pushback
Institutional pushback is a common challenge for student activists. Universities may impose restrictions on protests or take disciplinary actions against participants. Navigating this pushback requires resilience, strategic thinking, and sometimes legal assistance.
Ensuring Inclusivity
Ensuring that the movement is inclusive and representative of diverse voices is crucial. Activist groups should strive to create spaces where all participants feel valued and heard. Inclusivity strengthens the movement and ensures that it addresses the needs and concerns of all community members.
Actionable Steps for Universities
Foster Open Dialogue
Universities should foster open dialogue by providing forums for discussion and debate. Encouraging open dialogue helps address the concerns of all stakeholders and promotes a culture of mutual understanding.
Review Investment Portfolios
Universities should review their investment portfolios regularly to ensure they align with their ethical standards and values. Engaging with students and faculty in this process can provide valuable insights and foster a sense of shared responsibility.
Support Student Initiatives
Supporting student initiatives through funding, mentorship, and resources can empower students to pursue their activism effectively. Universities should recognize the value of student activism as a critical component of academic life.
Conclusion
The recent wave of campus protests highlights the growing engagement of students and faculty in political activism. These protests, driven by a diverse coalition of participants, call for justice and solidarity with Palestinian rights while raising broader issues of freedom of speech and institutional response to dissent. As we navigate these complex times, it is essential to recognize the power of student movements and the potential for meaningful change within our academic institutions.
For those interested in taking action, understanding your rights, staying informed, and building alliances are crucial steps. Universities, too, have a role to play in fostering open dialogue, reviewing their policies, and supporting student initiatives. Together, we can create a more just and inclusive academic community.
For further resources and ways to get involved, consider reaching out to organizations like the ACLU, exploring academic journals, and engaging with community groups dedicated to social justice and activism. The journey toward justice and equity is ongoing, and every voice matters.