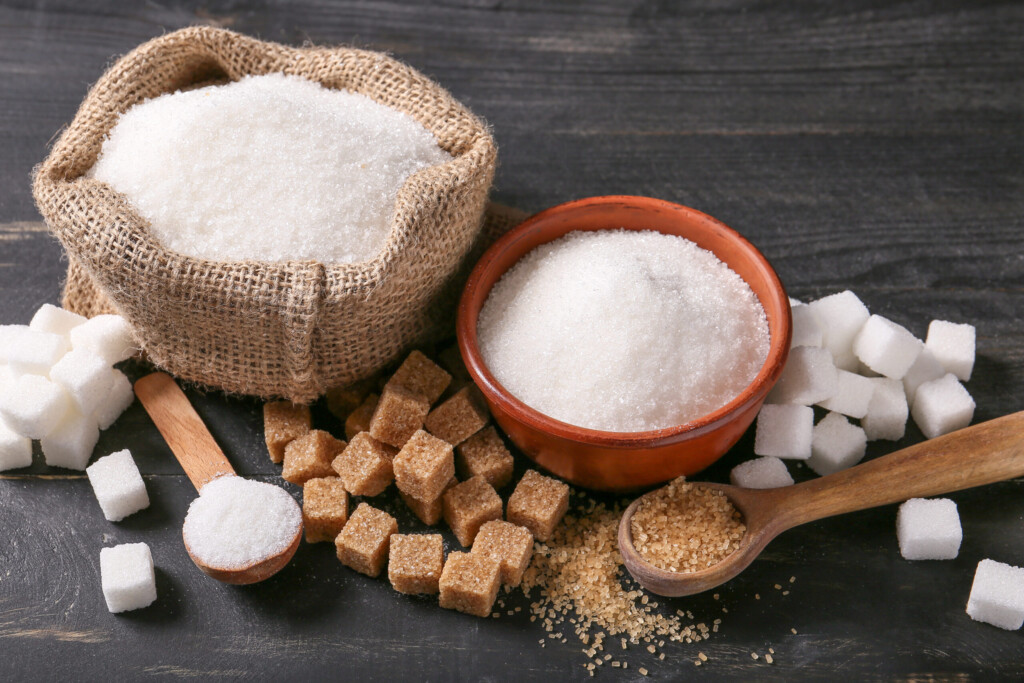
When it comes to making dietary choices, most of us recognize the need to limit one particular ingredient: added sugars. These are the extra sweeteners and syrups commonly found in products like sodas and cookies. While the occasional indulgence in a sugary treat is unlikely to be harmful, regular consumption of excessive added sugar can lead to a range of health issues.
What Happens When You Consume Too Much Sugar?
- Blood Sugar Fluctuations: Consuming too many simple carbohydrates, like sugar, can cause your blood sugar to rapidly rise and fall. This might result in feelings of nausea, fatigue, shakiness, or even a rapid heartbeat.
- Weight Gain: Sugary foods are often low in satiety, meaning they don’t keep you full for long. This can lead to an increase in hunger and a decrease in appetite-suppressing hormones, often resulting in weight gain. In fact, a 2019 study linked high sugar consumption to rising obesity rates.
- Dental Health Issues: Sugar is a leading cause of cavities. It feeds harmful bacteria in your mouth, which produce acids that erode tooth enamel and dentin. Reducing sugar intake is a crucial step in maintaining good dental health.
- Increased Inflammation: A diet high in sugar can contribute to inflammation, an underlying cause of various health issues like autoimmune diseases and inflammatory bowel diseases. A 2022 study highlighted the link between dietary sugars and inflammation, especially when combined with processed foods.
- Heart Disease Risk: Excessive sugar intake is linked to an increased risk of heart disease. A Harvard study from 2014 found a correlation between high sugar consumption and cardiovascular disease mortality.
- Skin Problems: High sugar intake can impact your skin’s appearance by creating advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which damage collagen and elastin. It can also exacerbate acne, as suggested by a study showing a 54% increased risk of acne with the consumption of fatty and sugary foods.
How Much Sugar is Too Much? The exact amount of sugar that’s too much varies depending on individual calorie needs. However, the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020 recommend limiting added sugars to no more than 10% of your daily calorie intake. The American Heart Association suggests an even lower percentage for optimal heart health.
Identifying Hidden Sugars To reduce sugar intake, check the “added sugars” line on nutrition facts labels when buying food. This will indicate the amount of sugar added during manufacturing.
Are There Benefits to Eating Sugar? Yes, in certain contexts. Sugar provides quick energy, beneficial for endurance athletes during long events. Also, it’s part of the joy of eating; savoring a sweet treat can be a delightful experience when done mindfully.
Healthier Alternatives and Swaps To reduce sugar intake, consider these swaps:
- Swap ice cream for Greek yogurt with berries and honey.
- Choose zero-calorie sparkling or fruit-infused water over soda.
- Opt for lower-sugar condiments like mustard or sriracha instead of ketchup or barbecue sauce.
- In baking, replace some sugar with alternative sweeteners like stevia.
- Choose low-sugar dark chocolate over sweeter candies.
- For breakfast, opt for oatmeal instead of sugary cereals.
In summary, while sugar can be part of a balanced diet, excessive consumption has significant health implications. Making mindful choices and swapping out high-sugar items for healthier alternatives can help mitigate these risks.